Economics Class 16
A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS (05:00 PM)
NAIROBI MINISTERIAL CONFERENCE (05:01 PM)
- The emergence of new issues-
- Some developing countries were attempting to categorize nations such as India and China as emerging economies instead of developing countries.
- Rich countries wanted to revitalize WTO by discussing new issues often called emerging trade issues.
- 1) e-commerce
- 2) Labor and environmental standards
- 3) Transparency in government procurement
- 4) Supply chain management
- 5) Transparency in state-owned enterprises and designated monopolies
- India's stand on new issues
- India has made it clear that it will not sign any binding agreements.
- The issues of labor and environment should be discussed under concerned international bodies such as ILO, and UNFCCC.
- India wanted developed countries to include human capital movement under the category of new issues
- India also wanted rich countries to drastically reduce their trade-distorting farm subsidy
- India wants on priority a permanent solution with respect to public stockholding.
- India was also looking for effective implementation of the package for LDCs including duty-free and quota-free market access
- Developed countries accepted to remove export subsidies with respect to agriculture with immediate effect and developing countries will do it by the year 2019 except for marketing and logistics subsidies (which will be removed by 2023).
BUENOS AIRES MINISTERIAL CONFERENCE (05:11 PM)
- It was held in 2017. It ended up without any declaration because of a lack of consensus.
- Emergence of pressure groups/ peer groups and they were discussing e-commerce. [discussion on the particular issue which was not related to trade]
- Fisheries-related subsidies- Preventing harmful fishery subsidy [signed in Geneva 2022]
- Women-related aspects/gender-related issues were brought
- India's stand- India said that the WTO platform should be used to discuss trade-related issues and not the other issues which can be discussed on the multilateral platform
GENEVA MINISTERIAL CONFERENCE (05:13 PM)
- [ * Marketplace model and Inventory based model
- Amazon is market place model and FDI is allowed in this. In some cases, Amazon promotes those companies in which it has a majority stake. Developing countries wanted to put restrictions on this. Whereas Developed countries wanted no restrictions. ]
- It was the 12th Ministerial conference
- 1) Agreement on COVID-19 vaccine production- WTO members agreed to temporarily waive intellectual property patents on COVID-19 vaccines without the consent of the patent holder for the next 5 years. The current agreement is a milder version of the original proposal made by India and south-Africa in 2020, where they were requesting a broader intellectual property rights waiver on vaccines, diagnostic services, treatment, etc
- 2) e-commerce transactions- India asked WTO members to review the extension of the moratorium on customs duties with respect to e-commerce transactions which included digitally traded goods and services. All the member countries agreed to continue the moratorium until the subsequent ministerial conference or March 31st, 2024 depending upon whichever comes first.
- 3). Curb harmful subsidies on illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing for the next 4 years- India and other developing countries were able to win some concessions with respect to this agreement i.e. traditional farmers would not face any restrictions under this agreement.
- Issues raised by India
- 1) Permanent solution with respect to Public stockholding.
- 2) Reserving Special and differentiated treatment [S&DT].
- 3) Another critical issue for India is that it is not allowed to export food grains from publicly held stocks.
AGREEMENT ON SANITARY AND PHYTO-SANITARY MEASURES (05:32 PM)
- It provides guidelines for member countries mainly to adopt measures related to food safety and plant & animal health from various biosafety risks arising from trade.
- These risks are usually related to pests and diseases and may arise due to the risk of toxins and contaminants in food and feed while importing items.
- Members can adopt restrictive measures under the SPS agreement, Thus SPS provides bio-security measures that are applied to protect human, animal, and plant life, or health.
- WTO gives detailed guidelines for protecting human or animal life or health and phytosanitary [Plant life/health] measures that may affect trade.
- SPS allows countries to set their own standards but SPS regulations must be based on science and they should be applied only to the extent necessary to protect human, animal, or plant life.
FISCAL POLICY (05:42 PM)
- Framework of the topics
- Taxes
- Types of Taxes (Direct and Indirect)
- Methodology of Taxation
- Constitutional areas with respect to taxing
- Article 270, Article 271, Article 268, Article 269, Article 269A, Article 279 A
- 80th CAA, 88th CAA, 101st CAA
- Types of Direct Taxation and Indirect taxation
- GST
- Different types of deficits- RD, ERD, Budgetary Deficit, Fiscal deficit, Primary deficit.
- Trends and pattern based question- Of 5 years
- FRBM Act and recommendations of N K Singh committee.
TERMINOLOGY RELATED TO FISCAL POLICY (05:50 PM)
- Fiscal policy is of the government and it deals with incoming money into the government's pocket (Receipts) and outgoing money from the government's pocket (Expenditure or payments).
- If the Receipts are more than the expenditure then it is called Surplus Budget.
- If the Receipts are less than the expenditure then it is called a deficit Budget.
- Two types of Fiscal policy-
- Expansionary Fiscal policy and Contractionary Fiscal policy
- Negative growth for two successive quarters- Recession. During a slowdown in the economy or a recession then we use the Expansionary fiscal policy.
- When expansionary policy is used then it may lead to inflation.
- Note- Government generally does not use the contractionary policy- Due to Election and populist policies, Also Fiscal policy is more direct and the people can understand the fiscal policy easily. [* Monetary policy impact is more indirect]
- Fiscal stimulus- The government is pumping money to revive the economy. It can be in the form of reducing the tax rate, increasing subsidies, Bail-out packages, etc
- After the fiscal stimulus, the Deficit will increase.
FISCAL POLICY (06:05 PM)
- It deals with revenues and expenditures of the government. The government follows an expansionary fiscal policy to increase economic growth (Move out of recession). Expansionary policy focuses on reducing tax rates, increasing subsidies, and also bail-out packages.
- Though expansionary fiscal policy may lead to an increase in economic growth, it will have a negative impact on inflation.
- Contractionary fiscal policy focuses on reducing government spending or expenditure. Excessive fiscal stimulus in the recent past has made monetary policy futile or ineffective.
- In countries like India, Fiscal policy plays an important role in increasing economic growth along with ensuring price stability.
- In developing economies like India, government spending is more than its revenue (Deficit Budget), thereby increasing the debt burden of the government.
- To handle the deficit, the government has to increase its revenue and reduce its expenditure and one of the most important forms of revenue is the tax source.
- Taxes (06:14 PM)
- Tax base- It is the reference for which we are calculating the tax. For excise duty, the reference is the production of goods. And for the income tax, the base is the income of the individual.
- Tax exemption- When exempted from paying tax. If there is an exemption of up to 3 lakhs then this exemption will be applied to all slabs. [* If income is 10 lakh also then also up to 3 lakhs the tax will be exempted]
- Tax rebate- The rebate is not across all the slabs. [* If the government is giving tax rebates up to 7 lakhs and one has a salary of 7.1 lakhs then up to 3 lakh the exemption will be applied and for the remaining amount the tax needs to be paid.]
- How to increase tax revenue?
- 1) In the short term, Government can increase tax revenue by increasing tax rates. [* Connect with the Laffers curve]
- 2) Government can also increase tax revenue by widening of Tax base
- 3) Increase tax efficiency or decrease tax inefficiency
- Seventh schedule- It contains the three lists- List I, List II, and List III.
- List I- Union list
- Taxes on income other than agricultural income.
- Duties of customs including export duties.
- Corporation tax, Capital Gains tax, Excise duty.
- Interstate sale of consignments
- Taxes on the capital value of the assets, exclusive of agricultural land, of individuals and companies and taxes on the capital of companies.
- Estate duty in respect of property other than agricultural land.
- Duties in respect of succession to property other than agricultural land.
- Terminal taxes on goods or passengers, carried by railway, sea or air, taxes on railway fares and freights.
- Taxes other than stamp duties on transactions in stock exchanges and futures markets.
- Rates of the stamp duty in respect of bills of exchange, cheques, promissory notes, bills of lading, letters of credit, policies of insurance, transfer of shares, debentures, proxies and receipts.
- Taxes on the sale or purchase of newspapers and on advertisements published therein.
- Taxes on the consignments of goods (whether the consignment is to the person making it or to any other person), where such consignment takes place in the course of inter-State trade or commerce.]
- List II- State list
- Taxes on agricultural income.
- Duties in respect of succession to agricultural land.
- Estate duty in respect of agricultural land.
- Taxes on lands and buildings.
- Taxes on mineral rights are subject to any limitations imposed by Parliament by law relating to mineral development.
- Duties of excise on the following goods manufactured or produced in the State and countervailing duties at the same or lower rates on similar goods manufactured or produced elsewhere in India- alcoholic liquors for human consumption and opium, Indian hemp, and other narcotic drugs and narcotics
- Taxes on the entry of goods into a local area for consumption, use or sale therein.
- Taxes on the consumption or sale of electricity.
- Taxes on goods and passengers carried by road or on inland waterways.
- Taxes on vehicles, whether mechanically propelled or not, suitable for use on roads, including tramcars subject to the provisions of entry 35 of List III
- Taxes on animals and boats.
- Tolls.
- Taxes on professions, trades, callings, and employment.
- Taxes on luxuries, including taxes on entertainment, amusements, betting, and gambling.
- Divisible Pool (07:14 PM)
- It is the pool from where the center shares the taxes with the states on the recommendation of the Finance Commission. Most of the important taxes were not part of the divisible pool
- 80th CAA 2000- Important taxes were also made part of the Divisible pool such as corporate taxes.
- Article 270- All taxes will be made part of a divisible pool except which are mentioned here-
- a) Article 268- It deals with all those taxes which are levied by the center but collected and used by the state.
- b) Article 269- All those taxes levied and collected by the center but given to states. For example interstate sales or interstate consignment movement. The Center will levy it and give it to states
- c) Article 269 A (101st Constitutional Amendment Act)- IGST system- Integrated Goods and Services tax
- d) Cess (Article 270) and Surcharges (Article 271)
- [Basic logic of surcharge is Tax on tax]
-
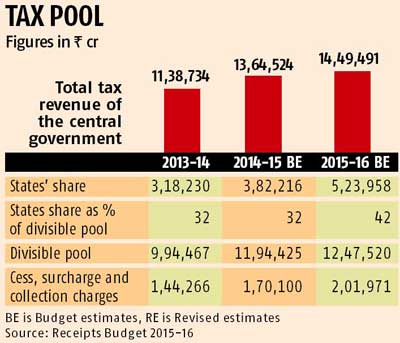
- The proportion of the cess and surcharges are increasing and this is not shared by the central government.
DEFINITION OF SOME TERMINOLOGY RELATED TO FISCAL POLICY (07:34 PM)
- Tax is a compulsory levy payable by an economic unit to the government without any corresponding entitlement to receive a definite and direct quid pro quo from the government.
- Taxes can be levied on income and expenditure.
- Examples- are personal income tax, corporate tax, etc.
- Taxes can also be levied in commodities( excise duty, customs), property and property transactions(wealth tax, estate duty,etc)
- Important terms
- Tax base
- The legal description of the object with reference to which the tax is payable.
- Example-base of excise duty is the production of commodities.
- The base of income tax is the income of the individual.
- Tax levy
- Levying or imposing a tax by an authority depends on the list in which a particular tax falls.
- All taxes mentioned in the Union List/ List I, the levy powers are with the center.
-
List I/ Central List List II/ State list Income tax except agriculture Agricultural income tax capital gains tax land revenue and property taxes Corporate tax Excise duty on Alcohol Stamp duties on financial documents Sales tax Customs duty Terminal taxes- Road, inland waterways Terminal tax Vehicles, boats, animals etc Excise duty - Most of the high revenue-giving taxes were part of the union list and states also had to perform developmental functions and therefore states were requesting for sharing of central taxes with the states.
- After the 80th Constitutional amendment, almost all important taxes of the center were made part of the Divisible pool of taxes, from which the center shares the revenues with the states based on the recommendations of the Finance Commission.
- After the 80th Constitutional amendment and the 10th Finance Commission recommendation, almost all the taxes were made part of the divisible pool except those mentioned under Article 270.
- Article 270 covers taxes mentioned under Article 268, Article 269, Article 269A, and Cesses & surcharges.
- Article 268- It deals with all those taxes levied by the center but collected and appropriated by states.
- Article 269- It deals with all those taxes which are levied and collected by the center but assigned to the states. Example- Interstate trade or sale, interstate consignment movement (From the manufacturer to the Franchise).
- Article 269A- It was introduced through the 101st Constitutional Amendment and it mainly deals with the IGST system.
- Tax on Tax/ cascading effect
- Suppose the price of a phone is 20000 and the government levied 10% as excise duty (2000) thus the cost is 22000.
- After this the state government also levied a 10% sales tax on 22000 which leads to 2200 (2000+200). This 200 is paid on already paid tax.
- This is called a tax on tax. It is an example of inefficient taxation and it is also called the cascading effect.
- In Dual GST system-
- If the tax rate is 20% then it will be equally divided into SGST and CGST i.e. 10% each. After that 10% CGST will be levied on the base price i.e. 20000 and 10% SGST will also be levied on the base price i.e. 20000. So the net tax will be 4000 and the final price will become 24000.
- In the GST system, the tax is levied on the same base thus the price of the final product will be 24000. [* The amount of 200 will be eliminated from the GST system]
- GST is a destination-based taxation
- Article 269- Interstate trade. The earlier center used to levy Central Sales tax. And this CST was credited to the exporter state.
- Article 269A- Whenever there is inter-state trade then IGST will be applied. It will be levied by the Center but it will be credited to the destination state (Importer state).
- IGST= CGST+ SGST
-
- The exporter states were not happy after the introduction of GST. Centers argument was that slowly the economic status of the destination state will improve and this promote cooperative federalism.
The Topic for the next class- GST.